Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
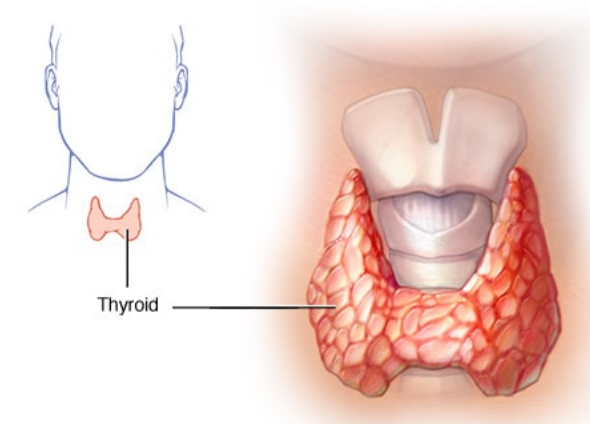
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) is a condition in which your thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine. Hyperthyroidism can accelerate your body's metabolism significantly, causing sudden weight loss, a rapid or irregular heartbeat, sweating, and nervousness or irritability. Several treatment options are available if you have hyperthyroidism. Doctors use anti-thyroid medications and radioactive iodine to slow the production of thyroid hormones. Sometimes, treatment of hyperthyroidism involves surgery to remove all or part of your thyroid gland. Although hyperthyroidism can be serious if you ignore it, most people respond well once hyperthyroidism is diagnosed and treated. Symptoms Hyperthyroidism can mimic other health problems, which may make it difficult for your doctor to diagnose. It can also cause a wide variety of signs and symptoms, including: Sudden weight loss, even when your appetite and the amount and type of food you eat remain the sam